
原文自国外Java社区javacodegeeks,作者为 Andy Beck,传送门
随着微服务的流行,我们在嵌入 servlet 容器应用程序中也看到了类似的现象。SpringBoot 是一款基于 java 的,应用程序服务式框架。它可以使用内嵌的 servlet 容器来运行独立的 jar 包或者作为 WAR 文件在容器中运行。
在这篇的例子中,我们将重点放在带有嵌入 servlet 容器的独立 jar 当中。框架支持三种不同种类的内嵌 servlet 容器:Tomcat(默认)、Jetty 和 undertow。我们将会比较这三者并且探讨在属性、配置、性能及内存使用中的区别。当中有很多优化性能和内存使用的方法,包括自定义自动配置以及组件扫描。
在这里我们使用 Erpingclipse Neon,Java 8,Maven 3.3.9,Spring 1.4.3,Tomcat 8.5.6,Jetty 9.3.14 和 Undertow 1.3.24。
1. 设置 SpringBoot 程序
我们在 Eclipse 中使用 maven来设置一个配置好适当依赖的新项目。在这个例子中,我们将使用 starter 父依赖但在生产环境中,我们可以根据情况去流程化、优化或者自定义配置。
1.1 配置 SpringBoot 依赖
tomcat 是 SpringBoot 项目中默认的内嵌 servlet 容器,Spring web 1.4.3 中使用的是 tomcat 8.5.6。
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- TOMCAT -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>1.2 配置 SpringBoot 主程序和控制器
在主类中加入 @SpringBootApplication 注解来配置 SpringBoot 程序。@SpringBootApplication 注解中包含 @SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration 和 @ComponentScan 这三个注解。
@SpringBootApplication
@ConfigurationProperties
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}你也可以去掉这个注解并只添加 @SpringBootConfiguration 来实现,或者使用另外一个类来做自定义配置。@ComponentScan 会扫描你的应用程序并且将用像 @Controller 注解配置的这样用于搭建 RESTful 服务的项添加进来。下面的控制器将从 HTTP GET 请求中返回一个简单的 “hello world” 字符串。
@Controller
public class SampleController {
@Autowired
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public String home() {
return "Hello World!";
}1.3 关键配置参数
所有的内嵌 servlet 容器的默认配置是相同的。一些需要考虑的重要属性是用于配置启动信息,譬如端口、应用名、TSL、访问日志、请求压缩等等。
例如,在配置 SSL 的时候将以下内容添加到 application.properties 的键值对中。
server.port=8443
server.ssl.key-store=classpath:keystore.jks
server.ssl.key-store-password=secret
server.ssl.key-password=another-secret1.4 如何找到额外的配置属性
为了探索更多 SpringBoot 的属性,你能添加 Spring actuator 依赖 并且在主类中添加 @ConfigurationProperties 注解。然后通过访问 /configprops 去获得可用的属性配置列表。
@SpringBootApplication
@ConfigurationProperties
public class Application {<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>http://localhost:8080/jcg/service/configprops1.5 更改内嵌 servlet 容器的版本
内嵌 servlet 容器的版本是被定义在 pom 的父依赖当中。你能通过显式包含依赖项并且在 pom 中定义新版本来更改内嵌 servlet 容器的版本。在下面来展示怎么去做。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>1.3.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>2. Tomcat
Tomcat 作为默认的内嵌 servlet 容器,在使用时不需要对默认的实现做任何额外的处理。你可以通过更改 pom.xml 或者 application.properties 配置来更改容器的版本。
2.1 更改 Tomcat 的版本
<properties>
<tomcat.version>8.5.6</tomcat.version>
</properties>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId>
<version>${tomcat.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-el</artifactId>
<version>${tomcat.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-websocket</artifactId>
<version>${tomcat.version}</version>
</dependency>3. Jetty
要将容器更改为 Jetty,你需要在 pom 文件中移除掉 Tomcat 依赖项并添加 Jetty。
3.1 更换为 Jetty(9.3.14 版本)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>4. Undertow
要将容器更改为 Undertow,你需要在 pom 文件中移除掉 Tomcat 依赖项并添加 Undertow。
4.1 更换为 Undertow(1.3.24 final 版本)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.undertow</groupId>
<artifactId>undertow-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.24.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.undertow</groupId>
<artifactId>undertow-servlet</artifactId>
<version>1.3.24.Final</version>
</dependency>5. 性能和负载
在下面,我们将分析这三个容器在 HTTP 请求的性能以及启动时的内存占用。我们使用 JMeter 通过模拟负载来测量性能,以及 JVisualVM 来查看内存占用。
5.1 性能测量
在下面,我们通过分析返回字符串的简单 RESTful GET 请求以及返回复杂 JSON 对象的 GET 请求来判断容器的性能。JMeter 是当中用来测量的工具。设置此次测试的关键是建立具有适当负载的线程组、动态更新 API 的输入的计数器以及显示汇总结果的报告。在字符串的示例中,我们使用一个包含1000个线程的线程组按顺序循环3次来执行,除此之外还使用10秒的 ramp up time。对于复杂对象的例子,我们使用相同的配置但不进行循环。
5.1.1 Tomcat
5.1.1.1 简单字符串
译者:解释下各个指标代表的意义。
- Label:样本名称;
- Samples:样本总数;
- Average:每个请求平均响应时间,单位毫秒;
- Min:最小响应时间;
- Max:最大响应时间;
- STD.DEV.:偏离量,越小表示越稳定;
- ERROR%:错误事务率;
- Throughput:吞吐量,每秒完成的请求数;
- Received KB/SEC:每秒从服务器端接收到的数据量;
- Sent KB/SEC:每秒发送的数据量;
- AVG. Bytes:平均数据流量;
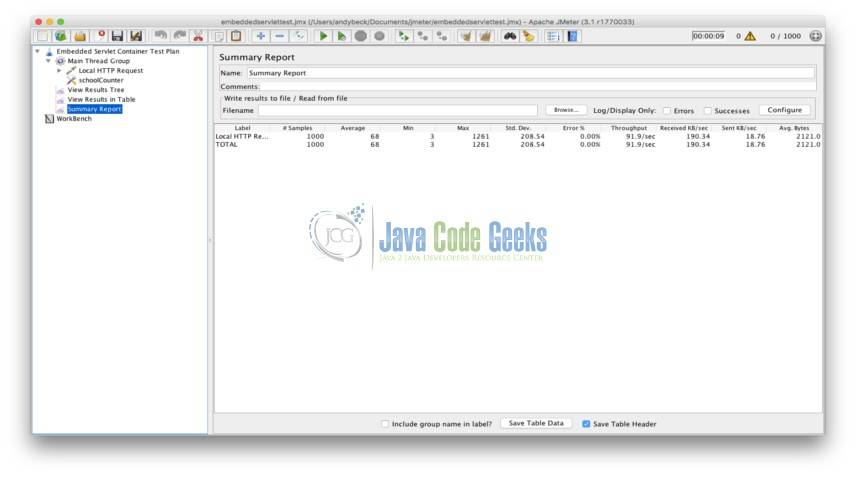
| Label | # Samples | Average | Min | Max | Std. Dev. | Error % | Throughput | Received KB/sec | Sent KB/sec | Avg. Bytes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Startup | 3000 | 7 | 1 | 549 | 35.78374361 | 0 | 293.8583603 | 55.95935572 | 55.67238466 | 195 |
| Others | 3000 | 1 | 0 | 45 | 1.359661682 | 0 | 287.8802418 | 54.82094449 | 54.53981144 | 195 |
| Others | 3000 | 1 | 0 | 24 | 1.155032275 | 0 | 292.1129503 | 55.62697785 | 55.3417113 | 195 |
5.1.1.2 动态数据的复杂对象
| Label | # Samples | Average | Min | Max | Std. Dev. | Error % | Throughput | Received KB/sec | Sent KB/sec | Avg. Bytes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Startup | 1000 | 114 | 3 | 1601 | 322.8671905 | 0 | 97.68486861 | 202.3335999 | 19.93763432 | 2121 |
| Others | 1000 | 3 | 2 | 17 | 1.328216473 | 0 | 97.88566954 | 202.7495167 | 19.9786181 | 2121 |
| Others | 1000 | 2 | 1 | 16 | 1.110529603 | 0 | 98.52216749 | 204.0678879 | 20.10852833 | 2121 |
| Others | 1000 | 2 | 1 | 21 | 1.344498419 | 0 | 98.53187506 | 204.0879951 | 20.11050966 | 2121 |
5.1.2 Jetty
5.1.2.1 简单字符串
| Label | # Samples | Average | Min | Max | Std. Dev. | Error % | Throughput | Received KB/sec | Sent KB/sec | Avg. Bytes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Startup | 3000 | 7 | 0 | 561 | 40.13705065 | 0 | 291.5168594 | 56.0828333 | 55.22878 | 197 |
| Others | 3000 | 1 | 0 | 21 | 1.058925031 | 0 | 293.5995302 | 56.48350338 | 55.6233485 | 197 |
| Others | 3000 | 1 | 0 | 21 | 0.926034317 | 0 | 294.3485086 | 56.62759395 | 55.7652448 | 197 |
5.1.2.2 动态数据的复杂对象
| Label | # Samples | Average | Min | Max | Std. Dev. | Error % | Throughput | Received KB/sec | Sent KB/sec | Avg. Bytes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Startup | 1000 | 110 | 3 | 1397 | 278.7961107 | 0 | 98.13542689 | 203.3626717 | 19.93375859 | 2122 |
| Others | 1000 | 3 | 2 | 20 | 1.500210319 | 0 | 98.48335631 | 204.0836739 | 20.00443175 | 2122 |
| Others | 1000 | 3 | 2 | 45 | 2.729377218 | 0 | 98.29942003 | 203.7025091 | 19.96706969 | 2122 |
5.1.3 Undertow
5.1.3.1 简单字符串
| Label | # Samples | Average | Min | Max | Std. Dev. | Error % | Throughput | Received KB/sec | Sent KB/sec | Avg. Bytes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Startup | 3000 | 6 | 0 | 451 | 31.6188702 | 0 | 295.6830278 | 63.81440346 | 56.01807363 | 221 |
| Others | 3000 | 1 | 0 | 22 | 1.255447862 | 0 | 292.7400468 | 63.17924839 | 55.46051669 | 221 |
| Others | 3000 | 1 | 0 | 18 | 1.559477975 | 0 | 294.3773918 | 63.53262069 | 55.77071681 | 221 |
5.1.3.2 动态数据的复杂对象
| Label | # Samples | Average | Min | Max | Std. Dev. | Error % | Throughput | Received KB/sec | Sent KB/sec | Avg. Bytes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Startup | 1000 | 70 | 3 | 1114 | 197.1333241 | 0 | 97.059109 | 203.3969361 | 19.62044201 | 2145.893 |
| Startup | 1000 | 42 | 3 | 852 | 132.6443576 | 0 | 98.02960494 | 205.6324135 | 20.00799554 | 2148 |
| Others | 1000 | 3 | 2 | 19 | 1.293570253 | 0 | 98.55129595 | 206.6305004 | 20.01823199 | 2147 |
| Others | 1000 | 2 | 2 | 27 | 1.659250132 | 0 | 98.74592673 | 207.0385788 | 20.05776637 | 2147 |
| Others | 1000 | 2 | 1 | 17 | 1.260904041 | 0 | 98.28975821 | 206.0821395 | 19.96510714 | 2147 |
5.2 内存测量
为了测量每个容器的内存,我们查看了启动时的内存使用情况。JVisualVM 是 Java 开发工具包中提供的一个工具,用于可视化 Java 应用程序的内存和内存占用使用情况。我们使用这个工具来显示三个容器初始启动冲击。堆大小和线程数是分析这个初始内存占用的关键。这三个容器都有的十个线程包括:JMX 服务器连接超时、RMI 调度器、RMI TCP 连接(2)、RMI TCP Accept、attach 监听器、DestroyJavaVM、信号分配器、Finalizer 以及 Reference Handler。
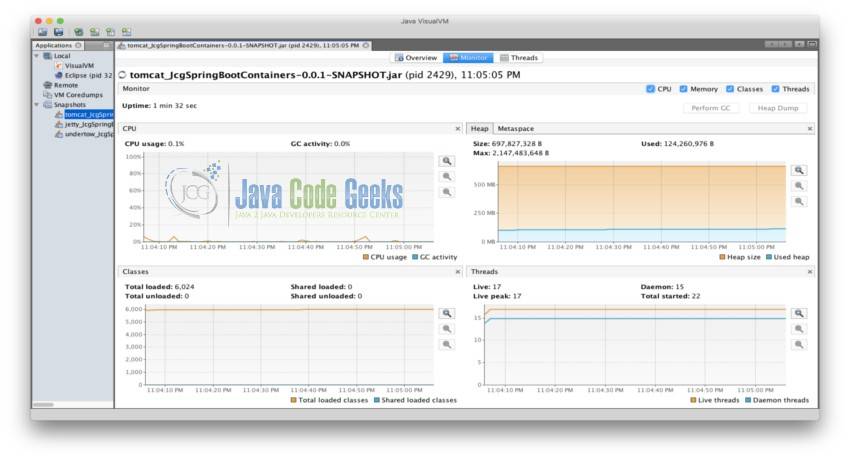
5.2.2 Tomcat
Heap Size: 697,827,328 B Used: 124,260,976 B Max: 2,147,483,648 B
Threads: 17 Live, 22 Started
5.2.3 Jetty
Heap Size: 628,621,312 B Used: 311,476,776 B Max: 2,147,483,648 B
Threads: 19 Live, 22 Started
5.2.4 Undertow
Heap Size: 630,718,464 B Used: 114,599,536 B Max: 2,147,483,648 B
Threads: 17 Live, 20 Started
6. 比较
6.1 性能
虽然在本例的参数测试中,所有三个容器都具有相似的性能,但是 Undertow 所表现得最好,Tomcat 和 Jetty 紧随其后。Jetty 在启动时占用内存最大,为311MB,Tomcat 和 Undertow 的初始占用内存很相似,大约为120MB,而 Undertow 最低为114MB。在响应头中关键的点在于,默认情况下,Undertow 是保持 HTTP 持久连接的。此头部将被用于支持持久连接的客户端,通过重用连接来优化性能。
6.1.1 Tomcat 响应头
Content-Type →application/json;charset=UTF-8
Date →Mon, 09 Jan 2017 02:23:26 GMT
Transfer-Encoding →chunked
X-Application-Context →JcgSpringBootContainers:# Application index.Jetty 响应头
Content-Type →application/json;charset=UTF-8
Date →Mon, 09 Jan 2017 02:29:21 GMT
Transfer-Encoding →chunked
X-Application-Context →JcgSpringBootContainers:# Application index.Undertow 响应头
Connection →keep-alive
Content-Type →application/json;charset=UTF-8
Date →Mon, 09 Jan 2017 02:20:25 GMT
Transfer-Encoding →chunked
X-Application-Context →JcgSpringBootContainers:# Application index.7. 结论
数字表明,Undertow 在性能和内存的使用方面是表现最好的。令人兴奋的是,它采用了最新的特性并且默认使用持久连接。基于本例子的负载,这些数字其实并没有显示出性能上的显著差异,但是我可以想象它们会作为一个标杆,并且如果性能是作为最重要的一点,那么 Undertow 会是你的应用程序的首要选择。还有一种合理的想法是,团队可能会因为熟悉某个容器的功能而选择使用它。并且很多时候,由于应用程序上的需要,包括性能、内存使用和功能性等等,需要更改容器的默认配置。
译者总结
最近无意中看到在 SpringBoot 的配置中,有一个名为 undertow 的配置,之前并没有听过关于这个容器相关的信息,于是在网上找了些资料,目前看到这篇对 SpringBoot 中支持的各个容器的性能对比,也借此了解了下 undertow,希望也能给到读者一点帮助。